Forex fund management refers to the practice of managing investment funds in the foreign exchange (forex) market on behalf of clients. It involves professionals or companies with expertise in forex trading who handle the investment decisions and trading activities of the fund.
Fund managers typically have extensive knowledge and experience in analysing currency markets, identifying trading opportunities, and executing trades. They aim to generate profits for their clients by taking advantage of fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
Below, I have listed an overview of how forex fund management typically works.
Fund Structure
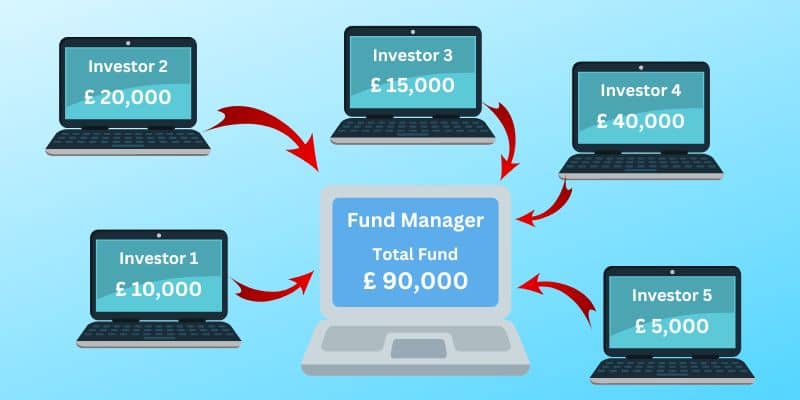
When it comes to the fund structure, fund supervisors typically set up a framework that allows them to pool funds from multiple investors who are interested in participating in the forex market. This structure provides a way for investors to gain exposure to the potential profits and risks associated with forex trading without having to actively manage their own trades.
There are a few common types of fund structures used by these investment professionals. One option is a managed account, where each investor has an individual account managed by the fund administrator. This allows for a more personalised approach as the fund manager can tailor their trading decisions to the specific goals and risk tolerance of each investor.
Another option is a pooled investment vehicle, such as a limited partnership or a hedge fund. In this case, investors contribute their funds to a single trading account, and their capital is combined. Each investor owns a proportionate share of the overall account based on their investment amount. This structure can provide greater diversification and potentially access to more sophisticated trading strategies.
Fund structures may have certain legal and regulatory requirements depending on the jurisdiction in which they operate. For example, hedge funds often have specific regulations regarding the number of accredited or qualified investors that can participate.
The fund structure is also influenced by factors like the minimum investment requirements, the frequency of investor contributions and redemptions, and the liquidity terms of the fund. Some funds may have lock-up periods during which investors cannot withdraw their funds, while others may allow for more flexible redemption options.
It’s worth mentioning that the fund structure is often outlined in the fund’s offering documents, such as a prospectus or private placement memorandum. These documents provide detailed information about the fund’s structure, investment strategy, fees, and other important aspects that potential investors should review before making any investment decisions.
The fund structure is designed to provide a framework for pooling investors’ funds, managing the trading activities, and ensuring proper governance and transparency. It’s crucial for investors to understand the structure and associated terms to make informed investment choices aligned with their financial goals and risk preferences.
If you want to compare performance results and fees of Forex Fund Management providers, follow the link below and fill out the form on the next page. You will receive up to 4 bespoke FREE quotes from top-ranking fund managers that best matches your requirements
Investor Contributions

When it comes to investor contributions, it’s all about investors putting their money into the managed account or investment vehicle managed by the company. This is how investors participate in the forex market without having to personally trade or monitor currency markets themselves.
Imagine you’re interested in forex trading, but you may not have the time, knowledge, or desire to actively trade currencies. That’s where a forex fund administrator comes in. They offer you the opportunity to invest your money in their managed account or investment vehicle, alongside other investors.
To get started, you would contribute a specific amount of money to the fund, which is typically a minimum investment threshold set by the company. They combine the contributions from all the investors into a single trading account, creating a pool of capital to work with.
Now, the proportion of the account that you own is based on the amount of money you’ve invested relative to the total capital in the fund. Let’s say you invest $10,000, and the total capital in the fund is $100,000. In this case, you would own 10% of the account.
They then uses this pooled capital to trade in the forex market on behalf of all the investors. They apply their expertise, trading strategies, and risk management techniques to make trading decisions and execute trades with the aim of generating profits for the fund.
As the administrator executes trades and manages the fund, they are responsible for monitoring market conditions, analysing currency trends, and adjusting the portfolio as necessary. They strive to maximise returns while managing risks within the predefined strategy.
It’s worth noting that investor contributions can vary depending on the specific forex fund and the terms set by the company. Some funds may have minimum investment requirements, while others may allow investors to contribute varying amounts based on their preferences.
Also, it’s important to remember that investing in forex funds carries risks. Forex markets can be volatile, and there’s always the potential for losses. That’s why it’s crucial to thoroughly research and understand the fund manager’s track record, investment strategy, and risk management practices before making an investment decision.
If you’re considering investing in a forex fund, it’s often a good idea to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalised guidance and help you assess the suitability of the investment for your specific goals and risk tolerance.
Trading Strategy

Trading strategy refers to a set of rules and techniques that traders use to make informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding financial instruments, such as stocks, currencies, or commodities. It’s like having a roadmap that guides their actions in the market.
Trading strategies can vary widely, and different traders adopt approaches that align with their individual goals, risk tolerance, and market preferences. Let’s explore some common trading strategies:
Trend Following
This strategy involves identifying and following trends in the market. Traders look for assets that are consistently moving in a particular direction and aim to enter positions in the same direction as the trend, hoping to ride the momentum and capture profits.
Breakout Trading
Breakout traders focus on price levels where the asset breaks through a significant support or resistance level. They anticipate that such a breakout may lead to a substantial price movement, and they enter positions in the direction of the breakout.
Range Trading
Range traders operate in markets that exhibit clear levels of support and resistance. They buy near support levels and sell near resistance levels, aiming to profit from the price bouncing within the defined range.
Scalping
Scalping is a short-term trading strategy where traders aim to make quick profits from small price movements. They execute multiple trades throughout the day, taking advantage of small price differentials and relying on high trading volumes and liquidity.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental traders base their decisions on analysing economic indicators, company financials, news events, and other factors that can impact the underlying value of an asset. They seek to identify undervalued or overvalued assets and take positions accordingly.
Technical Analysis
Technical traders focus on analysing historical price and volume data to identify patterns, trends, and potential entry or exit points. They use various technical indicators and chart patterns to guide their decision-making process.
It’s worth noting that trading strategies can be combined or customised based on individual preferences. Additionally, risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders or position sizing, are crucial aspects of any trading strategy to help mitigate potential losses.
Successful trading requires continuous learning, adaptability, and discipline. Traders often refine their strategies over time and adjust them to changing market conditions. It’s important to understand that no strategy guarantees profits, and traders should always be aware of the risks involved and use proper risk management techniques.
Remember, if you’re considering trading or investing, it’s a good idea to start with a solid understanding of the markets, seek education and guidance, and be prepared to invest time and effort into developing your skills and knowledge.
If you want to compare performance results and fees of Forex Fund Management providers, follow the link below and fill out the form on the next page. You will receive up to 4 bespoke FREE quotes from top-ranking fund managers that best matches your requirements
Trade Execution

Trade execution refers to the process of placing and completing trades in financial markets. In the context of forex trading, trade execution involves executing buy or sell orders for currency pairs at the desired price and time.
When a forex trader decides to enter or exit a position, they submit an order to their broker or trading platform. The order specifies the currency pair, the desired quantity (lot size), and the price at which they want to execute the trade. There are generally two types of orders used in trade execution:
Market Orders
A market order is executed at the current market price. When a trader places a market order, they are essentially telling the broker to execute the trade immediately at the prevailing market price. Market orders are typically used when traders want to enter or exit a position quickly, without specifying a specific price.
Limit Orders
A limit order is an order to buy or sell at a specific price or better. If the current market price reaches the specified limit price, the trade is executed. Limit orders allow traders to be more precise with their entry and exit points. For example, if a trader expects a currency pair to reach a certain level before reversing, they can place a limit order at that specific price level.
Once the order is submitted, the broker or trading platform processes it and attempts to match it with a counterparty willing to take the opposite side of the trade. In the forex market, trades are usually executed electronically, and the matching process occurs within seconds.
Trade execution can be influenced by various factors, including market liquidity, volatility, and the speed of order processing. In highly liquid markets, such as major currency pairs, trade execution is usually fast and efficient. However, in less liquid markets or during periods of high volatility, trade execution may experience delays or slippage, which is when the executed price differs from the requested price.
To ensure effective trade execution, forex traders often use tools like stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and trailing stops. These tools help manage risk and automate trade exits based on predetermined conditions, such as reaching a certain profit target or limiting potential losses.
It’s worth noting that trade execution is a critical aspect of forex trading, as it directly impacts the entry and exit prices of trades. Efficient trade execution can minimise costs, optimise profit potential, and help traders implement their trading strategies effectively. Traders should choose reputable brokers or trading platforms that offer reliable and fast trade execution to enhance their trading experience.
Performance Reporting

Performance reporting is a crucial aspect of forex fund management that allows investors to assess the progress and success of their investments. It provides a snapshot of how the fund has performed over a specific period and helps investors make informed decisions about their financial goals.
The performance report typically includes various metrics and information that highlight the fund’s performance. Here are some key elements you might find in a performance report:
Returns
Returns indicate the profits or losses generated by the fund during a specific time frame. It’s usually presented as a percentage to help investors understand the relative performance. Positive returns indicate profits, while negative returns suggest losses.
Benchmark Comparison
In performance reports, fund managers often compare the fund’s performance to a benchmark index or industry standards. This allows investors to gauge how well the fund has performed compared to the broader market or a specific set of investment parameters.
Risk Metrics
Risk metrics provide insights into the level of risk associated with the fund’s investment strategy. Metrics such as standard deviation, Sharpe ratio, or drawdowns may be included to help investors assess the volatility and potential downside of their investment.
Trade History
Performance reports may include a breakdown of the fund’s trade history, including the positions entered and exited during the reporting period. This information helps investors understand the trading activity and the decisions made by the fund manager.
Portfolio Allocation
A performance report may outline the allocation of the fund’s capital across different currencies, trading strategies, or risk levels. This provides transparency regarding how the fund manager has diversified investments and managed risk within the portfolio.
Commentary and Insights
Fund managers often include commentary or insights on market conditions, economic events, or specific trades that influenced the fund’s performance. This narrative helps investors understand the context behind the numbers and gain a deeper understanding of the fund’s performance drivers.
It’s worth mentioning that performance reports are typically provided on a regular basis, such as monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the fund’s reporting cycle. These reports serve as a means of communication between the fund manager and the investors, enabling transparency, accountability, and informed decision-making.
Investors should carefully review performance reports, considering both the historical performance and the fund manager’s investment strategy. It’s important to note that while performance reports provide valuable information, they cannot guarantee future results. Therefore, it’s advisable to analyse performance reports alongside other factors and consult with financial professionals before making investment decisions.
If you want to compare performance results and fees of Forex Fund Management providers, follow the link below and fill out the form on the next page. You will receive up to 4 bespoke FREE quotes from top-ranking fund managers that best matches your requirements
Fee Structure

The fee structure is an important aspect to consider. Typically, the company will charge two types of fees: a management fee and a performance fee.
The management fee is a percentage of the assets under management (AUM). It is calculated based on the total amount of capital that investors have entrusted to the administrator. This fee covers the costs associated with managing the fund, conducting market research, executing trades, and providing ongoing reporting to investors. The management fee is usually charged annually or quarterly and typically ranges from 1% to 2% of the AUM. However, the specific percentage can vary depending on the company and the investment strategy employed.
The performance fee, also known as a profit-sharing fee, is an additional fee that is based on the profits generated by the fund. It is designed to align the interests of the fund administrator with those of the investors. The performance fee is typically calculated as a percentage of the profits above a certain benchmark or hurdle rate. For example, they may charge a performance fee of 20% on profits generated above a specified annual return of, let’s say, 10%. This means that the company will only receive a performance fee if they surpass the predetermined benchmark return.
It’s worth noting that the performance fee is a way for fund managers to be rewarded for generating positive returns for investors. However, it’s important to carefully evaluate the performance fee structure and understand the terms and conditions associated with it. Some investors prefer fee structures that incorporate high-water marks or hurdle rates to ensure that the fund manager is incentivised to recoup any losses before earning a performance fee.
The fee structure can vary among companies and funds. It’s crucial for investors to carefully review and understand the fee structure, including both the management fee and the performance fee, and assess them in relation to the potential returns and risks associated with the fund. It’s always a good idea to consult with a financial advisor who can help analyse the fee structure and provide guidance on the suitability of the investment.
It’s important to note that investing in forex funds involves risks, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Potential investors should carefully assess the fund administrator’s track record, investment strategy, risk management practices, and fee structure before making an investment decision. It’s advisable to consult with a financial advisor or conduct thorough due diligence before investing in any forex fund.
If you want to compare performance results and fees of Forex Fund Management providers, follow the link below and fill out the form on the next page. You will receive up to 4 bespoke FREE quotes from top-ranking fund managers that best matches your requirements

